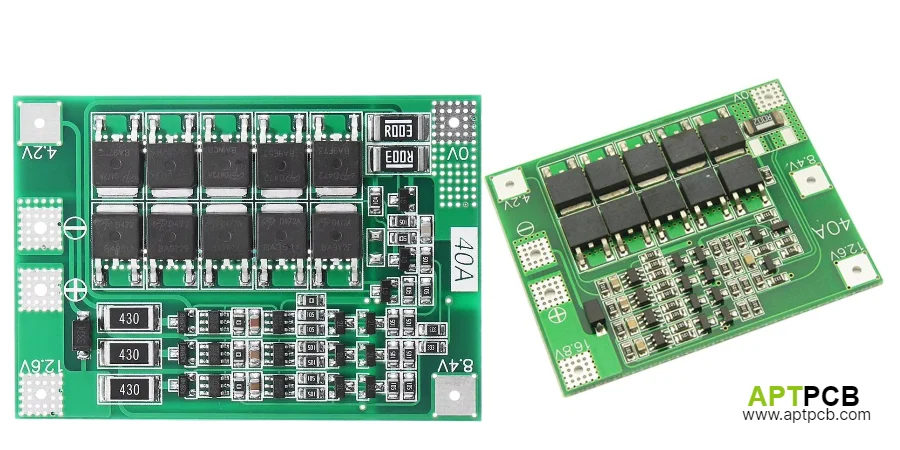
Battery Management System (BMS) PCB assemblies serve as the intelligence and safety backbone of lithium-ion battery packs, continuously monitoring individual cell voltages, temperatures, and pack current while coordinating charging, balancing, and protection functions. Modern BMS designs must achieve measurement accuracy within ±5mV across 4-100+ series-connected cells, execute protection responses within microseconds, and maintain reliable operation through 2000-5000 battery cycles spanning 10-15 years across automotive, energy storage, and industrial applications.
At APTPCB, we deliver comprehensive BMS PCB design and assembly services combining precision analog design expertise, high-reliability manufacturing processes, and validated functional testing. Our capabilities support diverse battery chemistries including NMC, LFP, and NCA cells across voltage ranges from 12V power tool batteries through 800V+ automotive traction packs and commercial energy storage systems.
Implementing Precision Cell Voltage Monitoring Architecture
BMS accuracy fundamentally determines battery pack performance, safety, and longevity. Voltage measurement errors propagate through state-of-charge (SOC) estimation causing premature charge termination (reducing usable capacity) or delayed protection activation (risking cell damage). High-performance BMS designs target ±3-5mV absolute accuracy across operating temperature ranges of -40°C to +85°C while handling common-mode voltages reaching hundreds of volts in high-voltage battery systems.
At APTPCB, our BMS assembly services implement proven analog front-end (AFE) architectures with validated calibration procedures ensuring measurement precision across production volumes.
Key Voltage Monitoring Design Requirements
Analog Front-End IC Integration
- Specialized AFE chips (TI BQ76952, ADI LTC6811, NXP MC33771) monitoring 6-18 cells per device with turnkey assembly component sourcing and placement
- Daisy-chain communication architecture enabling scalable systems monitoring 100+ cells with isolated differential interfaces
- Built-in cell balancing drivers, temperature inputs, and GPIO functionality reducing external component count
Precision Reference and ADC Design
- Temperature-compensated voltage references maintaining <10ppm/°C drift ensuring measurement stability across automotive temperature ranges
- High-resolution delta-sigma ADCs (16-24 bit effective) achieving sub-millivolt resolution after digital filtering
- Proper reference decoupling and routing techniques preventing noise coupling from digital switching into analog measurement paths
Cell Connection and Filtering
- RC filtering on cell voltage inputs (typically 100Ω + 100nF) rejecting high-frequency switching noise while limiting input current during fault conditions
- Balanced differential routing maintaining matched trace lengths and impedance minimizing common-mode to differential conversion
- Strategic component placement with PCB conformal coating application protecting high-impedance analog inputs from humidity and contamination
Temperature Compensation and Calibration
- Factory calibration procedures measuring offset and gain errors at multiple temperatures with calibration parameters stored in non-volatile memory
- Software algorithms compensating for systematic errors improving absolute accuracy from typical ±10-15mV to ±3-5mV specification levels
- Production testing quality validation verifying each BMS meets accuracy specifications before shipment
Common-Mode Voltage Isolation
- Isolated power supplies and communication interfaces enabling AFE chips operating at battery pack potential (0-800V relative to vehicle ground)
- Proper PCB layout with special PCB manufacturing creepage and clearance maintaining safety isolation >2.5kV between high-voltage and low-voltage sections
- Differential communication (SPI, I2C) transmitted through isolated interfaces (capacitive or transformer-based) maintaining data integrity despite common-mode transients
Diagnostics and Self-Test Capabilities
- Built-in voltage reference checks and ADC self-calibration routines detecting measurement drift or component failures
- Cross-checking between redundant sensors or measurement paths enabling fault detection and safe shutdown before hazardous conditions develop
- Comprehensive functional testing during manufacturing validating diagnostic capabilities and fault response
Validated Measurement Accuracy and Reliability
Through precision AFE integration, validated calibration procedures, and comprehensive testing implemented via our quality system controls, APTPCB delivers BMS assemblies achieving industry-leading measurement accuracy supporting optimal battery utilization and safety across demanding automotive and industrial applications.
Executing Cell Balancing for Pack Capacity Optimization
Cell voltage imbalances develop naturally during battery operation due to manufacturing variations, temperature gradients, and aging differences between cells. Without active balancing, pack capacity becomes limited by the weakest cell—when the lowest-capacity cell reaches minimum voltage during discharge, the BMS must stop discharging even if other cells retain significant energy. Similarly, during charging, the highest-capacity cell reaches maximum voltage first, prematurely terminating charge and preventing other cells from reaching full capacity.
APTPCB implements comprehensive balancing solutions optimizing pack energy utilization and extending battery lifetime.
Key Cell Balancing Implementation
Passive Balancing Circuits
- Resistor-based dissipative balancing bleeding excess energy from higher-voltage cells as heat during charge or rest periods
- MOSFET switches (controlled by AFE chip GPIO) connecting bypass resistors (typically 50-100Ω, 1-2W) across targeted cells
- Component sourcing of appropriately-rated resistors and MOSFETs handling continuous power dissipation at elevated temperatures
- Thermal management through strategic resistor placement and adequate copper pour area spreading heat dissipation
- Typical balancing currents: 50-200mA per cell sufficient for correcting imbalances during extended charge periods
Active Balancing Topologies
- Capacitive or inductive charge transfer circuits moving energy from higher-voltage to lower-voltage cells improving overall efficiency
- Flyback or resonant converter topologies enabling bidirectional energy transfer during charge, discharge, or rest periods
- Higher component count and cost justified for applications requiring fast balancing or high efficiency (premium EVs, stationary storage)
- Custom magnetics design and NPI assembly prototyping validating performance before production commitment
Balancing Control Algorithms
- Threshold-based balancing activating when cell voltage differences exceed 10-50mV targets preventing excessive over-balancing energy waste
- Temperature-aware control reducing or disabling balancing at elevated temperatures preventing thermal runaway risk
- SOC-based balancing scheduling focusing balancing efforts during charge periods when voltage differences are most pronounced
- Dynamic current allocation maximizing balancing throughput while respecting thermal limits of individual cells and overall pack
Thermal Integration and Safety
- Temperature sensors placed near balancing resistors providing thermal feedback to control algorithms preventing component overheating
- PCB conformal coating protecting balancing circuits while accommodating localized heat dissipation requirements
- Overcurrent and thermal shutdown circuits providing fail-safe protection if balancing MOSFET failures cause short circuits
- Production incoming quality control screening resistors and MOSFETs for tolerance and thermal characteristics ensuring consistent balancing performance
Balancing Performance Monitoring
- Real-time tracking of balancing current and energy dissipated per cell enabling diagnostic insight into cell health and degradation patterns
- Historical logging of balancing activity identifying cells requiring excessive balancing indicating capacity loss or high self-discharge
- Communication of balancing status through CAN bus enabling system-level optimization and predictive maintenance strategies
Optimized Pack Energy Utilization
By implementing appropriate balancing strategies validated through mass production processes and comprehensive testing, APTPCB enables BMS assemblies maximizing usable pack capacity, extending cycle life, and supporting optimal battery system economics across diverse applications.
Providing Multi-Layer Battery Protection Circuits
Lithium-ion battery safety depends on multi-layer protection preventing dangerous operating conditions including overcharge (risking thermal runaway), over-discharge (causing capacity loss or copper dissolution), overcurrent (generating excessive heat), and short circuits (potentially causing fires). BMS protection circuits must respond within microseconds to fast-developing fault conditions while avoiding false trips during normal operation including cold-temperature starting, regenerative braking, or fast charging.
APTPCB implements comprehensive protection strategies supporting automotive functional safety requirements and industrial reliability standards.
Key Protection Implementation Requirements
Voltage-Based Protection Functions
- Overvoltage protection (OVP) comparing individual cell voltages against maximum thresholds (typically 4.2-4.3V for NMC cells) with fast detection (<10ms) and immediate charge disconnect
- Undervoltage protection (UVP) preventing deep discharge below minimum safe voltage (typically 2.5-2.7V) where irreversible damage occurs
- Hysteresis and delay settings preventing oscillation during voltage recovery after protection activation
- Hardware backup protection using independent voltage comparators providing redundant safety layer if primary monitoring fails
Current-Based Protection Functions
- Charge overcurrent protection (COCP) monitoring pack current against maximum charging rate specifications (typically 1-3C for consumer cells)
- Discharge overcurrent protection (DOCP) detecting excessive discharge currents during acceleration, motor starting, or load shorts
- Multi-stage current limiting providing graduated response: warning at 90% threshold, power reduction at 100%, hard cutoff at 110-120%
- Fast short-circuit detection (<10μs response) immediately opening contactors before fault current causes cell damage or fire
Temperature-Based Protection
- Multiple NTC thermistors distributed throughout pack monitoring cell surface temperatures and critical hot spots
- Charge temperature limits (typically 0-45°C) preventing lithium plating during low-temperature charging or thermal stress during high-temperature charging
- Discharge temperature limits (typically -20 to +60°C) protecting cells from excessive heating during high-power discharge
- Thermal runaway detection comparing rapid temperature rise rates triggering emergency shutdown and external alarm signals
Contactor Control and Arc Suppression
- High-reliability contactors (rated >100k mechanical cycles, >10k electrical cycles at full load) isolating battery from load during fault conditions
- Pre-charge circuits limiting inrush current when connecting battery to discharged system capacitances preventing contact welding
- Soft-start strategies gradually applying battery voltage reducing mechanical stress on contactors and downstream electronics
- Arc suppression through controlled contactor opening sequences and possible active arc extinction circuits for high-power applications
Redundancy and Fail-Safe Design
- Independent monitoring ICs providing redundant voltage and current measurement detecting primary BMS failures
- Hardware watchdog circuits forcing safe state if microcontroller firmware crashes or communication timeouts occur
- Mechanical safety devices (fuses, current limiters, thermal fuses) providing last-resort protection if all electronic protection fails
- Comprehensive testing and quality validation verifying protection activation at specified thresholds across production units
Certified Protection Performance
Through multi-layer protection implementation validated via rigorous testing protocols and supported by our quality inspection procedures, APTPCB delivers BMS assemblies meeting automotive functional safety standards (ISO 26262 ASIL-C/D), UL 2580 battery safety requirements, and IEC 62619 industrial battery standards.
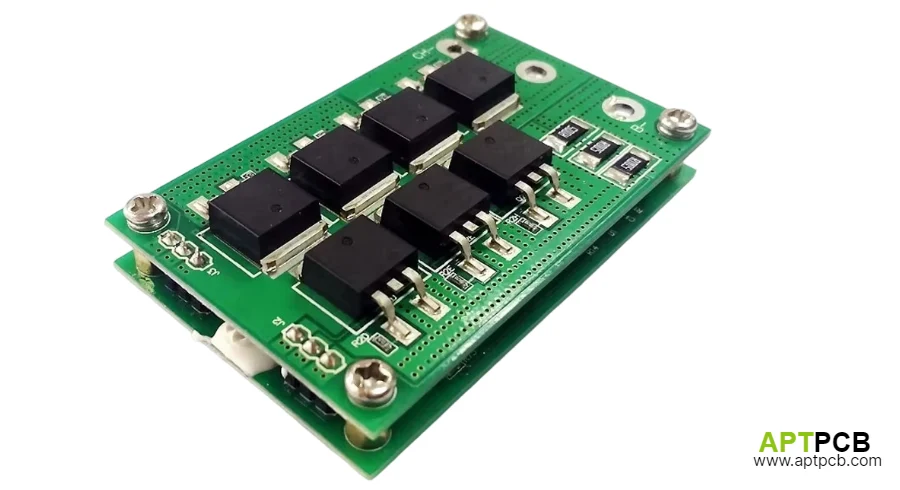
Integrating CAN Bus Communication and System Coordination
Modern battery systems require comprehensive communication enabling BMS coordination with vehicle controllers (automotive), energy management systems (storage), or machine controllers (industrial equipment). Robust communication interfaces ensure safe system operation, enable advanced features including regenerative braking coordination and state-of-charge-based power management, and support diagnostic capabilities reducing service costs through predictive maintenance.
APTPCB implements industry-standard communication protocols with validated electrical specifications and comprehensive testing.
Key Communication Integration Features
CAN Bus Interface Implementation
- Automotive-grade CAN transceivers meeting ISO 11898 electrical specifications providing robust differential signaling immune to electromagnetic interference
- Proper termination networks (120Ω resistors at bus ends) ensuring signal integrity and preventing reflections on longer cable runs
- ESD protection structures safeguarding transceivers from cable discharge events during hot-plugging or electrostatic exposure
- SMT assembly precision ensuring reliable transceiver mounting and signal integrity through controlled impedance routing
Protocol Stack and Message Formatting
- CANopen, J1939, or custom protocols defining message structures, object dictionaries, and state machine behavior
- Real-time transmission of critical parameters: individual cell voltages, pack current, state-of-charge, state-of-health, temperature extremes
- Periodic heartbeat messages enabling system-level fault detection if BMS communication fails
- Event-triggered messages providing immediate notification of fault conditions, protection activation, or diagnostic codes
Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Support
- Comprehensive fault code definitions (DTC - Diagnostic Trouble Codes) identifying specific failure modes aiding service technicians
- Historical data logging recording events leading to protection activation enabling root cause analysis of field failures
- Calibration parameter access through service tools allowing factory or field adjustment of protection thresholds and balancing settings
- Firmware update capability through CAN bootloader enabling feature enhancements and bug fixes without hardware replacement
Isolation and Safety Considerations
- Galvanic isolation between high-voltage battery pack and low-voltage vehicle CAN bus maintaining safety barriers >2.5kV
- Isolated DC-DC converters powering BMS electronics from high-voltage battery preventing ground loops affecting measurement accuracy
- Differential signaling and twisted-pair cabling providing common-mode noise rejection critical in high-EMI automotive and industrial environments
- Validation through automotive EMC testing (ISO 11452 radiated immunity, ISO 7637 conducted transients) ensuring reliable operation
Alternative Communication Interfaces
- SPI or I2C interfaces for local communication between master BMS controller and slave AFE chips in large battery systems
- RS-485 for longer-distance communication in stationary energy storage applications where CAN bus distance limits (40m at 1Mbps) are restrictive
- Wireless interfaces (Bluetooth, WiFi) enabling convenient monitoring and configuration through smartphone apps or web dashboards
- Ethernet integration for grid-scale energy storage requiring high-bandwidth communication to SCADA systems
Validated Communication Reliability
Through proper interface implementation, comprehensive protocol testing, and validation procedures supported by our proven manufacturing capabilities, APTPCB delivers BMS assemblies achieving robust communication performance supporting safe, efficient battery system operation across diverse applications.
Supporting Diverse Battery Configurations and Chemistries
Battery management requirements vary significantly across applications and cell chemistries. Automotive traction batteries demand high-power handling (200-400kW), fast charging support (800V architecture, 350kW DC fast charging), and functional safety certification (ISO 26262). Energy storage systems prioritize long cycle life (6000-10000 cycles), precise SOC/SOH estimation for warranty and grid services, and modular scalability to megawatt-hour capacities. Industrial equipment requires rugged operation in harsh environments (-40°C cold starting, +70°C continuous), vibration resistance, and long service life (10-15 years) without maintenance.
APTPCB provides flexible BMS manufacturing supporting diverse requirements through configurable designs and scalable production.
Key Application Flexibility Capabilities
Chemistry-Specific Parameterization
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): Lower nominal voltage (3.2V), flatter discharge curve requiring advanced SOC algorithms, superior thermal stability, 4000+ cycle life
- Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC): Higher energy density, steeper voltage curves simplifying SOC estimation, thermal management critical, 1500-3000 cycles
- Lithium Titanate (LTO): Ultra-fast charging capability, wide temperature range (-30°C to +55°C), 10000+ cycle life, lower energy density
- Configurable voltage thresholds, temperature limits, and charging profiles optimized for specific cell chemistry and manufacturer specifications
Scalable System Architectures
- Modular AFE designs supporting 4-16 cells per circuit board with daisy-chain expansion to 100+ cell systems through master-slave configurations
- Distributed BMS topologies placing monitoring and balancing circuits close to cells reducing wiring complexity in large battery packs
- Centralized BMS architectures consolidating intelligence in single controller reducing cost for smaller battery systems (12-48V power tools, backup power)
- Flexible assembly accommodating custom connector types, mounting configurations, and thermal interface requirements
Power Level Optimization
- Low-power monitoring circuits (<1mA quiescent current) enabling long-term storage mode for infrequently-used battery systems
- High-current contactor drivers and gate drive circuits (100-500A continuous, 1000A+ peak) supporting high-power automotive and industrial applications
- Thermal management strategies from natural convection (small packs) through forced air cooling and liquid cooling interfaces (EV and ESS applications)
- Testing validation including thermal chamber testing, vibration qualification, and accelerated life testing simulating years of field operation
Certification and Compliance Support
- Design documentation, DFMEA, and test reports supporting automotive IATF 16949 quality management and functional safety assessments
- Material declarations (RoHS, REACH, conflict minerals) enabling global market access and OEM supply chain compliance
- First article inspection documentation with dimensional verification, electrical testing, and material traceability supporting customer PPAP requirements
- Manufacturing quality records and certificates of conformance demonstrating production consistency and traceability for audit and warranty purposes
Engineering Support and Customization
- Application engineering assistance with cell selection, pack configuration, and BMS specification development
- Custom firmware development implementing customer-specific algorithms, communication protocols, or safety features
- DFM collaboration optimizing designs for manufacturability, cost reduction, and supply chain resilience
- Ongoing technical support through support services including troubleshooting, failure analysis, and continuous improvement programs
Comprehensive BMS Solutions
By combining technical expertise, flexible manufacturing capabilities, and comprehensive quality management, APTPCB enables battery manufacturers, automotive OEMs, and energy storage developers deploying safe, reliable BMS solutions optimized for specific application requirements and market positioning.
Delivering Scalable Production from Prototypes to Volume Manufacturing
BMS development programs require responsive manufacturing supporting rapid design iterations during development, flexible pilot production for customer sampling and certification testing, and cost-effective volume manufacturing maintaining consistent quality as production ramps to thousands or millions of units annually.
APTPCB provides complete BMS manufacturing services from concept through production with consistent processes and dedicated engineering support.
Key Production Capabilities and Services
Rapid Prototype Development
- NPI assembly services delivering functional BMS prototypes in 7-10 days supporting design validation, software development, and integration testing
- Engineering collaboration reviewing schematics, PCB layouts, and bill-of-materials identifying potential issues before first article build
- Flexible assembly accommodating design changes, component substitutions, and test fixture modifications during development without excessive lead time or cost penalties
- Initial functional testing validating core BMS functions (voltage monitoring, protection activation, communication) providing early feedback on design performance
Pilot Production and Validation
- Small-batch manufacturing (10-100 units) providing customer samples for system integration testing, regulatory testing, and market evaluation
- First article inspection with comprehensive dimensional verification, electrical testing, and functional validation documenting manufacturing capability
- Process validation including reflow profiling, automated optical inspection programming, and functional test development establishing repeatable production methods
- Engineering support during certification testing assisting with test preparation, troubleshooting failures, and implementing design improvements based on test results
Volume Manufacturing and Quality Assurance
- Mass production capability supporting volumes from 1,000 to 100,000+ units annually with consistent quality and competitive pricing
- Automated assembly equipment including high-speed pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and in-line inspection systems ensuring repeatable processes
- Statistical process control monitoring critical parameters (reflow temperatures, component placement accuracy, test yields) enabling proactive quality management
- Comprehensive quality systems meeting automotive IATF 16949, ISO 9001, and industry-specific standards providing confidence in long-term supply
Supply Chain Management and Continuity
- Strategic component sourcing managing long-lead-time parts (AFE chips, contactors, connectors) and securing allocations during supply shortages
- Authorized distributor relationships ensuring authentic components with full traceability preventing counterfeit risks critical for automotive and safety applications
- Buffer inventory strategies and alternative component qualification protecting against supply chain disruptions and supporting responsive delivery
- Obsolescence management proactively monitoring component lifecycles and implementing replacements before end-of-life situations create production disruptions
Ongoing Engineering and Support Services
- Cost reduction initiatives identifying opportunities for material standardization, alternative components, or process optimization reducing per-unit costs
- Quality improvement programs analyzing field failures, implementing corrective actions, and feeding learning back into design guidelines
- Manufacturing engineering support troubleshooting production issues, optimizing test procedures, and maintaining equipment calibration
- Customer communication and program management providing visibility into production schedules, quality metrics, and delivery performance
Reliable BMS Manufacturing Partnership
Through comprehensive manufacturing capabilities spanning development through volume production, supported by dedicated engineering resources and proven quality systems, APTPCB enables BMS developers and battery manufacturers focusing on innovation and market success while we deliver reliable, cost-effective assemblies meeting stringent automotive, industrial, and energy storage requirements.