Flex CAM Engineering & DFx Review
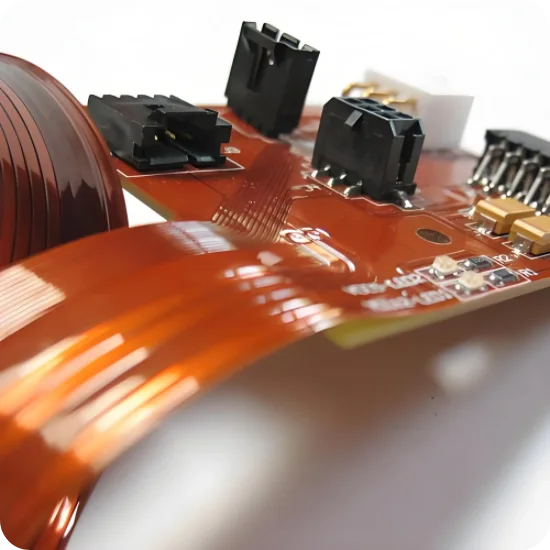
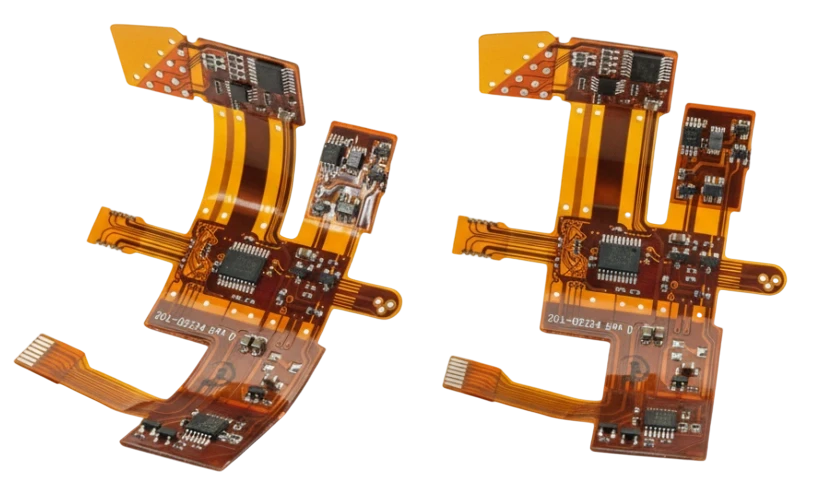
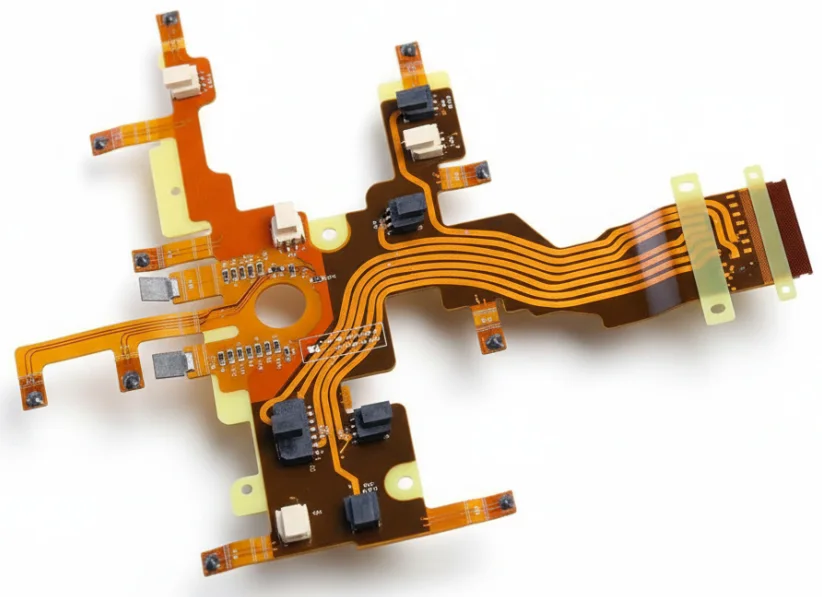
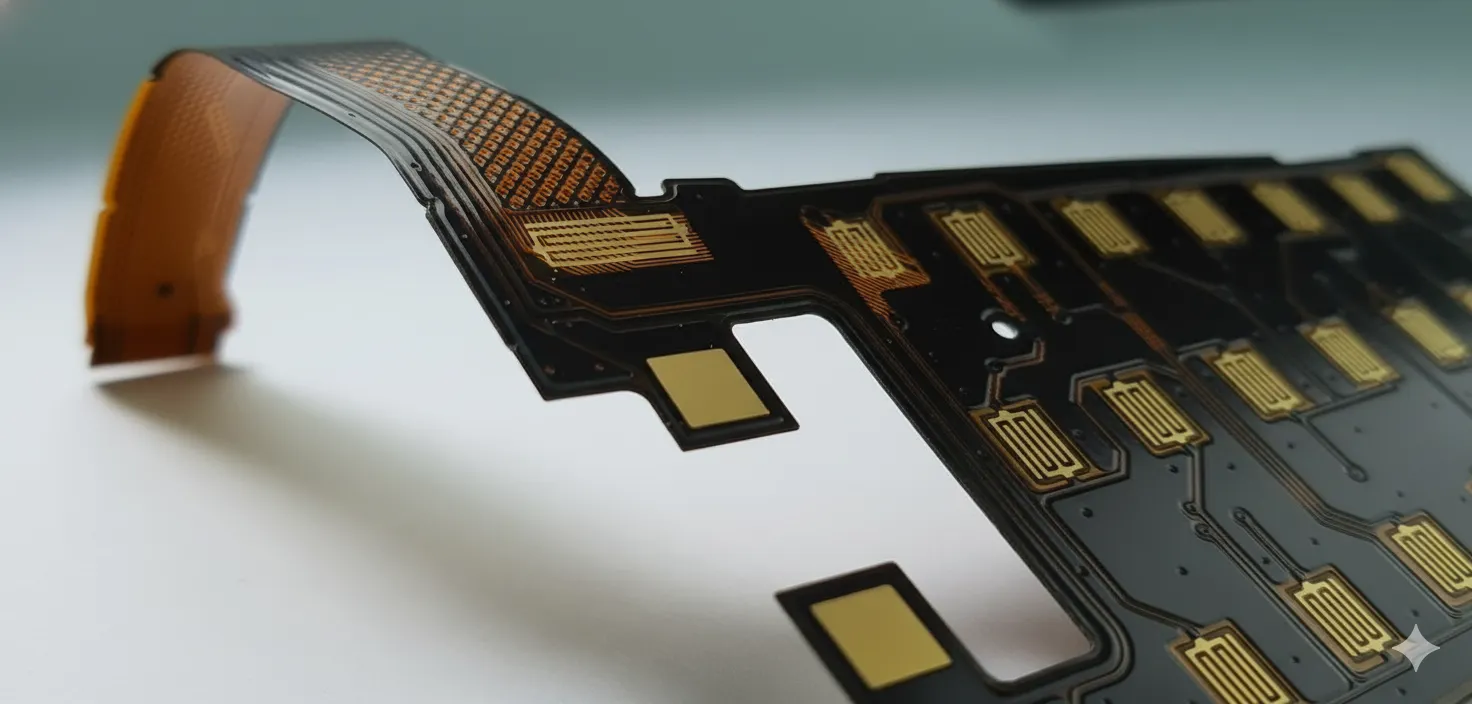
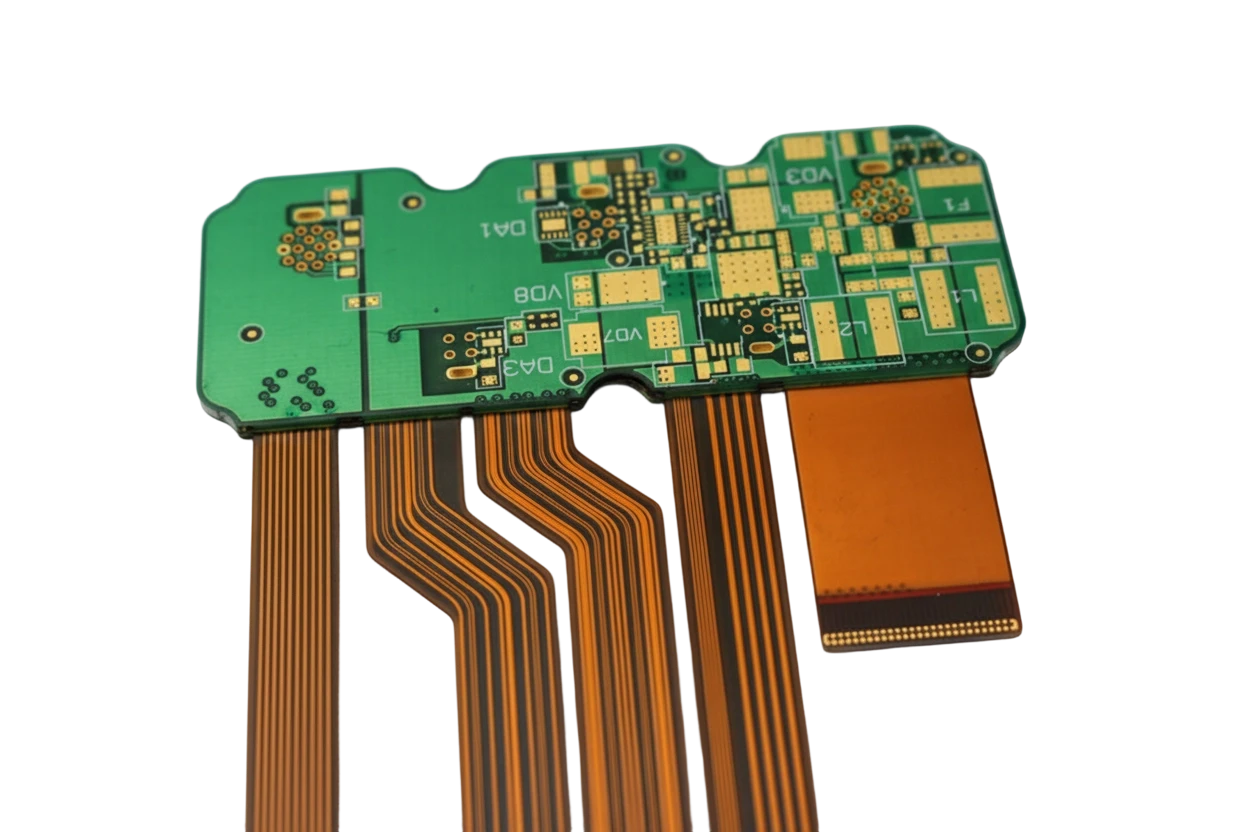
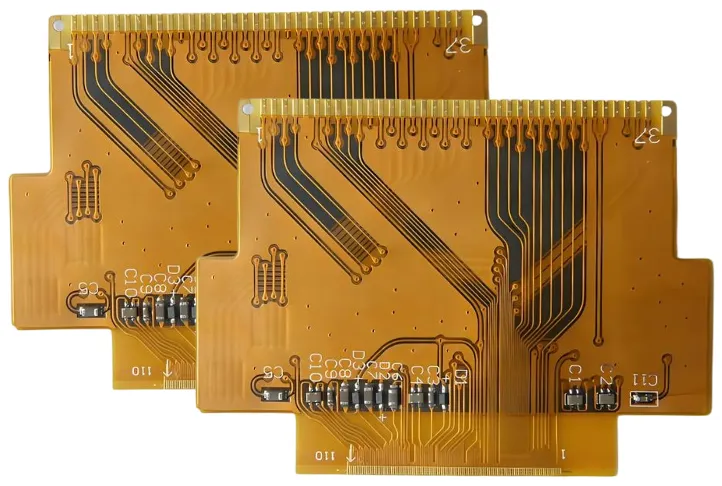
CAM engineers extract bend stack-ups, impedance targets, and stiffener callouts from ODB++ files, then create relief patterns, hatched grounds, and carrier tooling before routing to production.
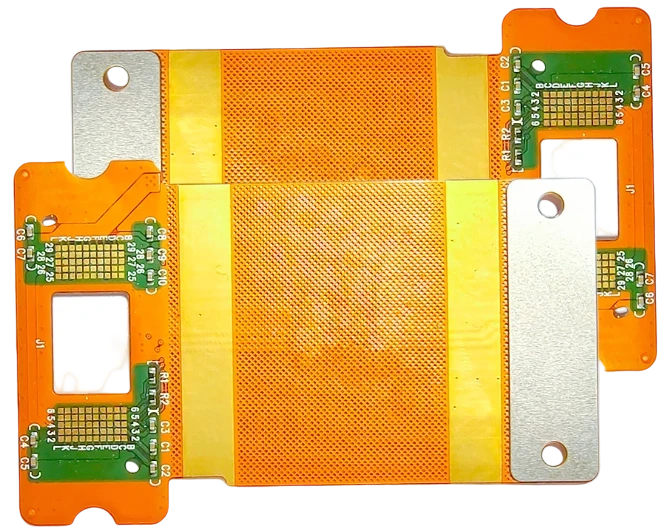
- Verify bend zones, neutral axis placement, and keep-out regions before tooling.
- Confirm stack-up thickness, copper grain direction, and impedance meshes for each layer.
- Generate coverlay relief, hatched grounds, and tear-stop features.
- Define stiffener outlines, PSA windows, and depth-controlled rout paths.
- Annotate impedance coupons, dynamic test coupons, and handling instructions.
- Optimize panel utilization with shared carriers and fiducials for SMT.
- Release fabrication notes covering bake cycles, cleanroom requirements, and packaging method.