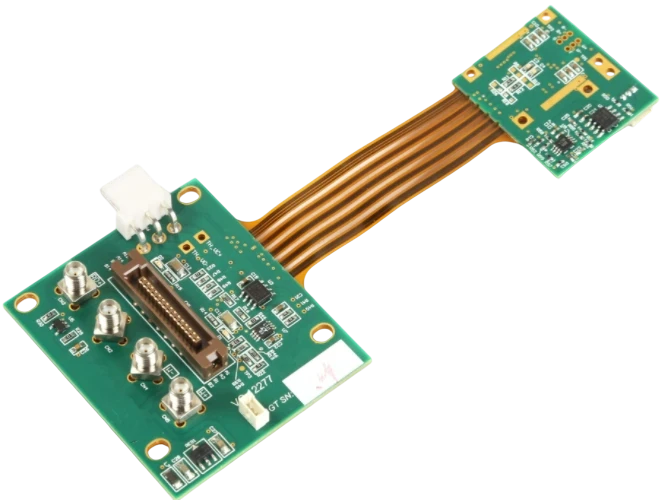
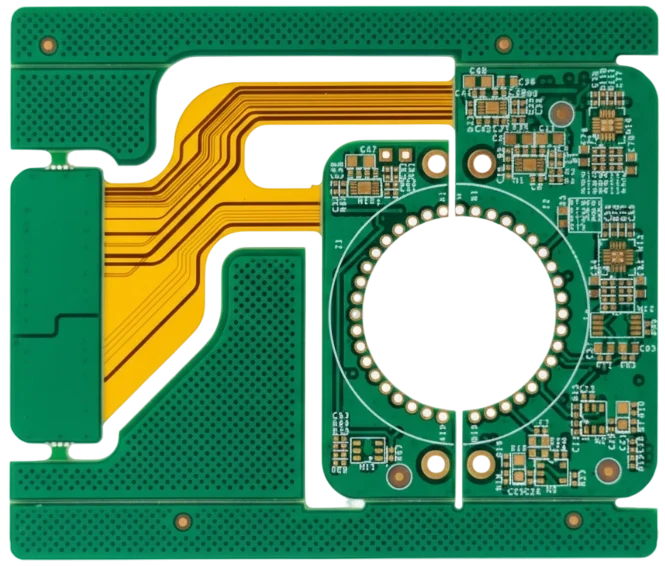
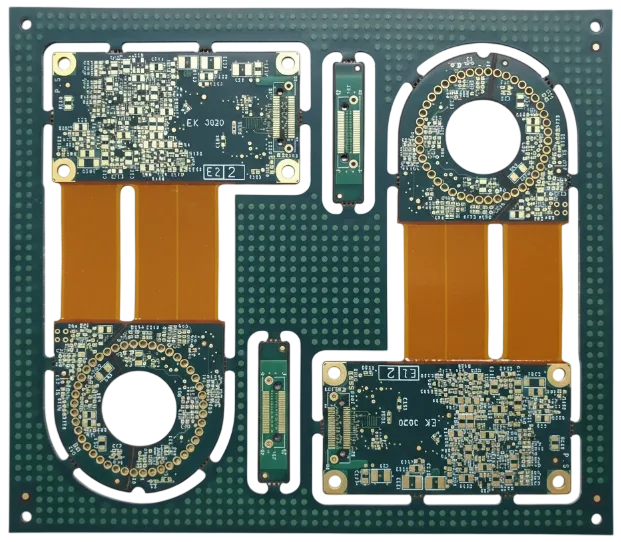
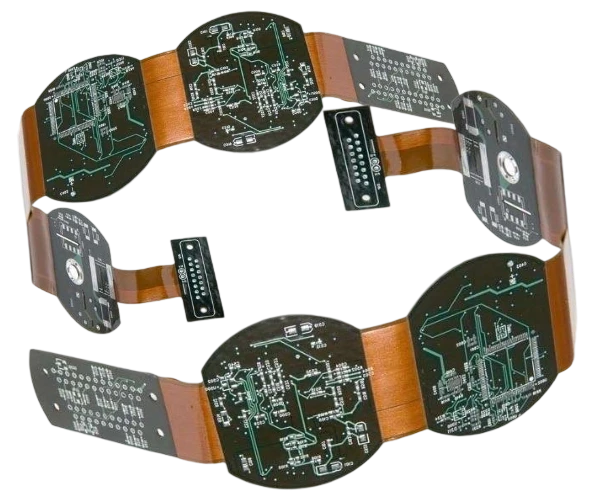
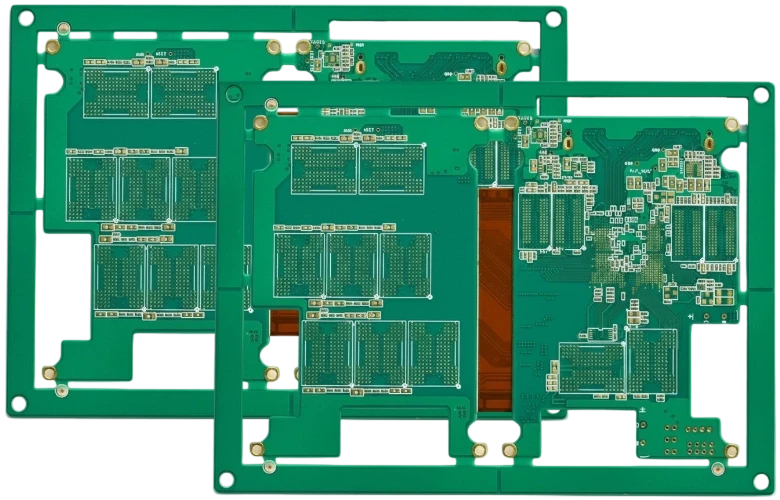
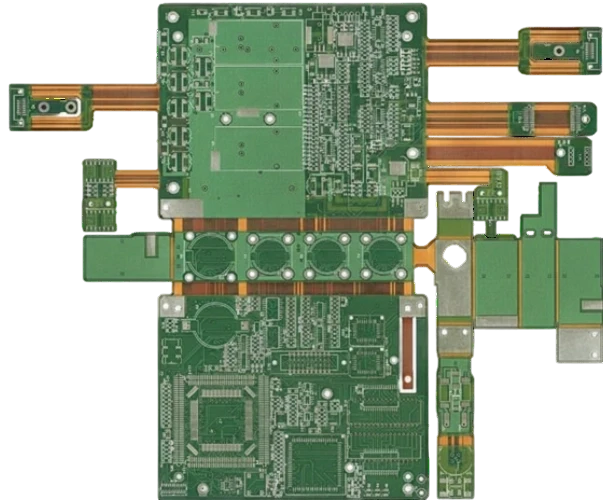
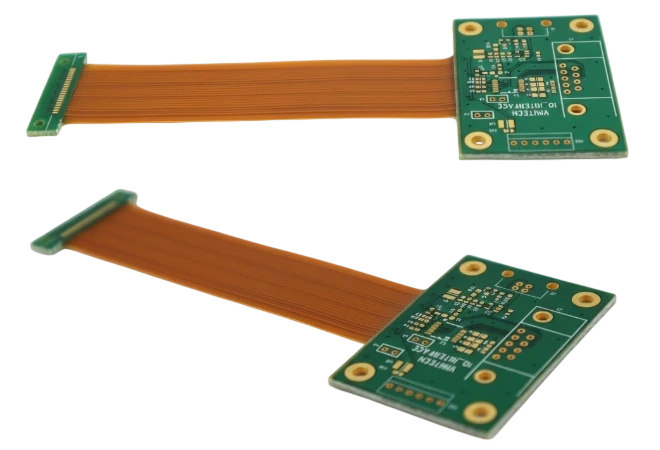
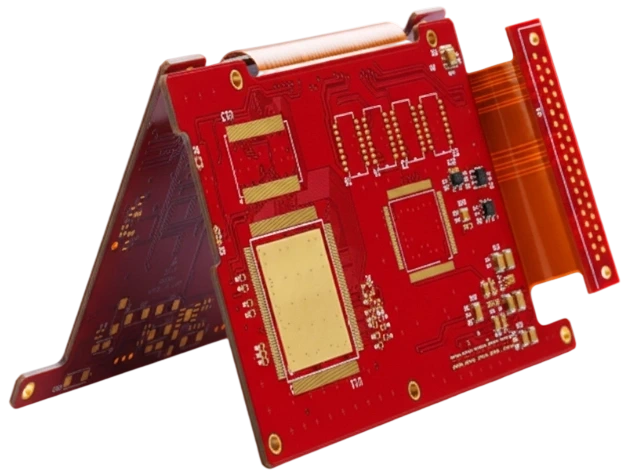
Rigid-Flex CAM & Stackup Engineering
CAM teams merge Gerber/Odb data with bend specs, define coverlay patterns, button plating, and impedance coupons, and align stackups with factory capabilities.
- Review IPC-2223 design constraints, bend radii, and keep-out zones.
- Align rigid/flex stackups with available copper weights and dielectric thicknesses.
- Define coverlay openings, teardrops, and hatched grounds for impedance stability.
- Specify button plating, staggered microvias, and back-drill locations.
- Plan stiffener outlines, PSA windows, and carrier tooling holes.
- Document impedance coupons plus dynamic flex coupons per lot.
- Release fabrication notes covering bake/lamination cycles and packaging.